Big Big Data
Digital Literacy and Online Safety (Y8) - Lesson 2
A note about this lesson

This lesson is taken from Common Sense Education’s excellent Digital Citizenship curriculum. Their resources are shared for free under A Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial- NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
You can find the original resources HERE.
Objectives
Lesson Resources
Lesson 1 - My Media Use: A Personal Challenge
Lesson 2 - Big Big Data
Lesson 3 - The Power of Digital Footprints
Lesson 4 - My Social Media Life
Lesson 5 - Upstanders and Allies
Lesson 6 - Copyright and Fair Dealing
Links to Education for a Connected World.
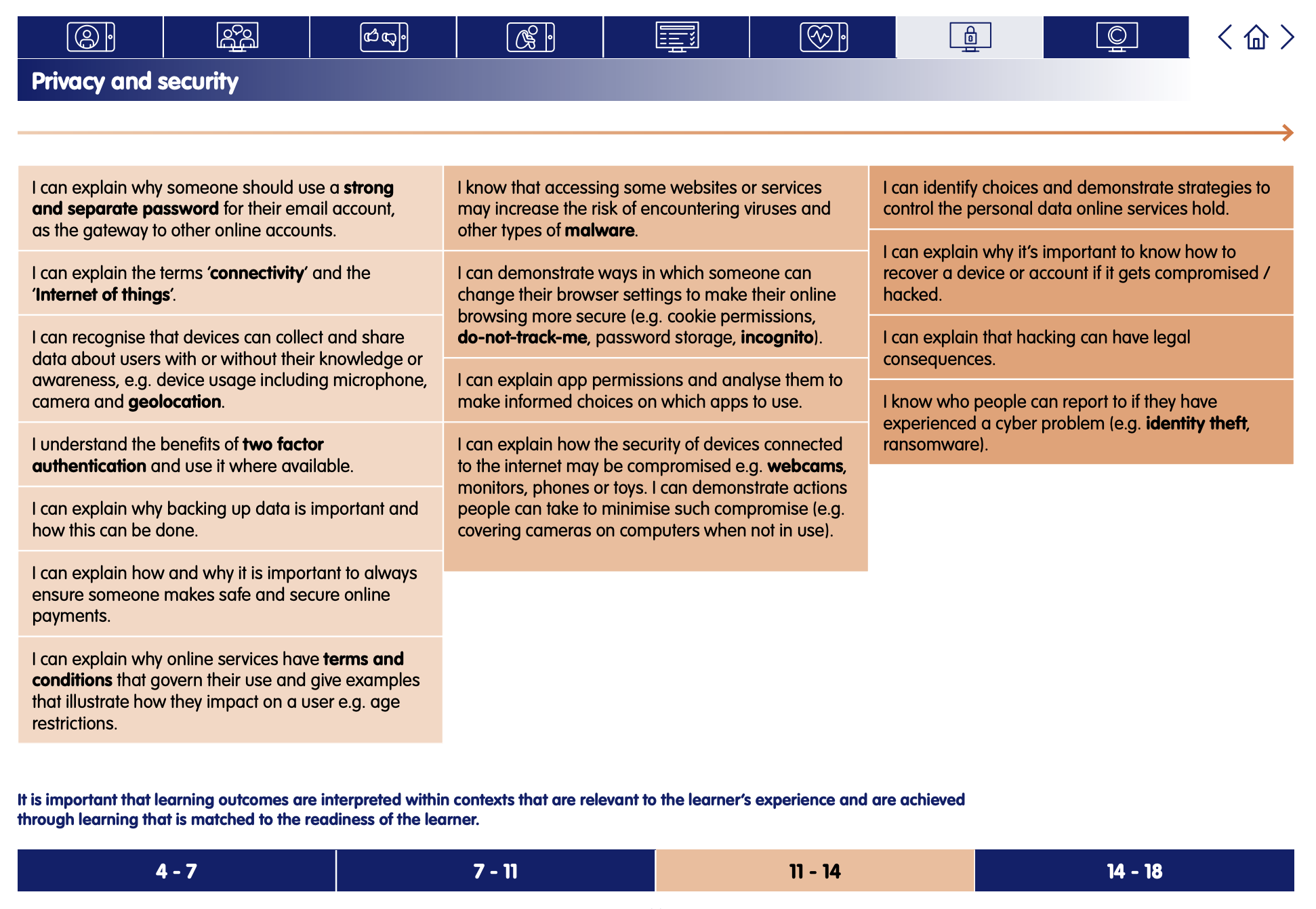
This lesson from Common Sense Media's Digital Citizenship curriculum links to the following strands from the Privacy and Security section of the Education for a Connected World framework.
Invite learners to share their ideas. Explain that the most important questions you might ask are related to teenagers themselves: What do they need? What do they like? What's important to them?
Invite learners to share their responses. Explain that companies often do surveys of consumers as well as focus groups (talking to people), and they look at online data. Define data as facts and statistics collected together to be used for different purposes. (Slide 6)
Invite learners to share their responses. Explain that one common type of data is online behavioural data: Companies want to know what their customers like to do, which sites they visit and which other products they buy. They use this information to design new products and to market existing products to new customers.
For example, if a company that makes cat food learns that a lot of their customers also buy dog food, they might start making dog food themselves, or they might start putting advertisements for dog food near the cat food, or they might do both.
- For Option 1, define cookies as small text files stored on a computer that keep track of what a person does on a website. (Slide 10)